Daniel Chodowiecki – The Polonica
Mediathek Sorted

![Ill. 2: Cabinet d’un peintre [Cabinet of a painter] Ill. 2: Cabinet d’un peintre [Cabinet of a painter] - Etching, 18 x 23 cm. Depicted is part of Chodowiecki's family.](/sites/default/files/styles/width_100_tiles/public/assets/images/2_mit_familie.jpg?itok=Ox3Ojmp4)






































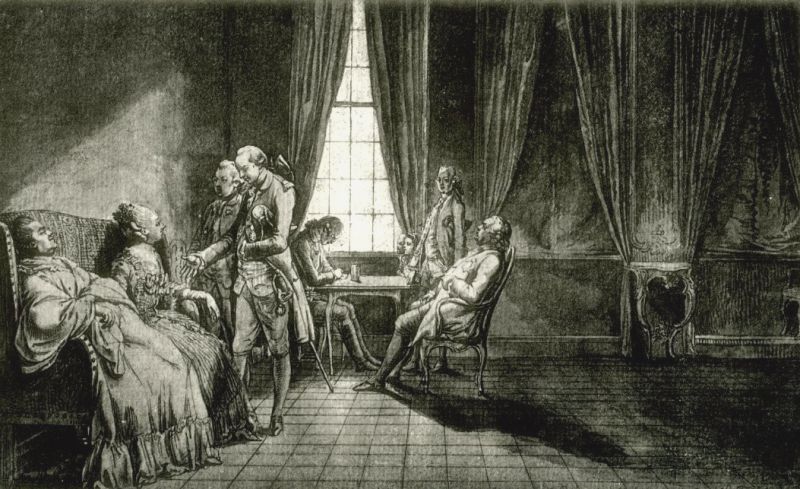
![Ill. 45: The new Polish Constitution Ill. 45: The new Polish Constitution - Etching, in: Begebenheiten aus der neueren Zeitgeschichte [...], Göttingen 1793.](/sites/default/files/styles/width_100_tiles/public/assets/images/45_polnische_verfassung.jpg?itok=8ZtNsUvt)
![Ill. 46: The celebration of Poland's great revolution Ill. 46: The celebration of Poland's great revolution - Etching, in: Sechs Blätter zur neueren Geschichte [...] 1793.](/sites/default/files/styles/width_100_tiles/public/assets/images/46_revolution_polens.jpg?itok=1TH3eNK0)

















Daniel Chodowiecki - Hörspiel von "COSMO Radio po polsku" auf Deutsch

![Ill. 2: Cabinet d’un peintre [Cabinet of a painter] Ill. 2: Cabinet d’un peintre [Cabinet of a painter] - Etching, 18 x 23 cm. Depicted is part of Chodowiecki](/sites/default/files/styles/width_100_tiles/public/assets/images/2_mit_familie.jpg?itok=Ox3Ojmp4)










































![Ill. 45: The new Polish Constitution Ill. 45: The new Polish Constitution - Etching, in: Begebenheiten aus der neueren Zeitgeschichte [...], Göttingen 1793.](/sites/default/files/styles/width_100_tiles/public/assets/images/45_polnische_verfassung.jpg?itok=8ZtNsUvt)



















In 1793 Chodowiecki wrote the following about his origins “To some extent I am also one of these good people [the respectable réfugiés who were forced to leave their fatherland 100 years ago and who were revered and loved everywhere they arrived, and who also did a lot of good in Germany], for my grandmother on my mother’s side was a réfugiée, although my father was a Polish citizen, a descendant of a courageous nation that will soon no longer exist.”[1] 1793 was the year of the Second Partition of Poland. The so-called réfugiés were therefore refugees, Huguenots, French Protestants who had been repressed by the clergy and monarchy in France since 1530. The Edict of Fontainebleau issued by Louis XIV in 1685 was as good as the equivalent of a ban on Protestantism. It triggered off the flight of a 250,000 Huguenots in the areas of Europe that were dominated by Protestants. Daniel’s mother, Marie Henriette Ayrer (*1702), came from a Huguenot refugee background on both sides of the family. According to Daniel, his Polish ancient ancestors could traditionally be traced back to the aristocrat Bartłomiej Chodowiecki, who lived in Greater Poland in the mid-16th century. But as early as the 17th century it was not possible to prove their aristocratic title, nor is it mentioned in Polish books on coats of arms.[2] Daniel’s direct forefathers were theologians and corn dealers in Thorn. His grandfather Christian (*1655) moved to Danzig because trading conditions were better there: here he ran a corn business that was taken over by his son, Gottfried/Godfryd (*1698). This was Daniel’s father. After Daniel’s parents were married they joined the Reformed Church in Danzig and orientated themselves around the culture of French immigrants. The upshot was that they spoke French. French was therefore Daniel Chodowiecki’s mother tongue. But he also spoke German and a little Polish. From their grandfather’s inheritance the family bought a house in Heiliggeistgasse.
Biography
Daniel Chodowiecki was born in Danzig (Gdansk) on 16th October 1726. He seemed to have had a happy childhood. One of his father’s hobbies was painting cameo portraits and he taught Daniel how to draw. After his father died in 1740 Daniel began training as an apprentice dealer in spices and food. Alongside these studies, and with the support of his aunt, he continued studying the art of drawing on his own initiative. In 1743, at the age of 16, like his younger brother before him, he moved to Berlin to work in the hardware store of his uncle Antoine Adrien Ayrer. Here both brothers made cameo copies of etchings, with which they decorated tins. In 1748/49 Daniel was taught enamel painting by the Augsburg copper engraver, Johann Jacob Haid (1704-1767). True, Daniel’s earliest extant drawing, “A Polish Jubilee year and Repentance Homily drawn in Kraków“ (1750), had a Polish motif, but it was probably a copy of a work by a man named Georg Christoph Kilian (1709-1781)[3] : it was entitled “A Polish Jubilee year and Repentance Homily drawn in Kraków“ (1750).[4] In 1754 he decided to become an artist in his own right, took up lessons in drawing from the Berlin history painter Bernhard Rode (1725-1797) and attempted to make contact with other successful young painters and etchers like Antoine Pesne, Joachim Martin Falbe and Blaise Nicolas Le Sueur, who became the director of the Berlin Akademie der Künste in 1756.
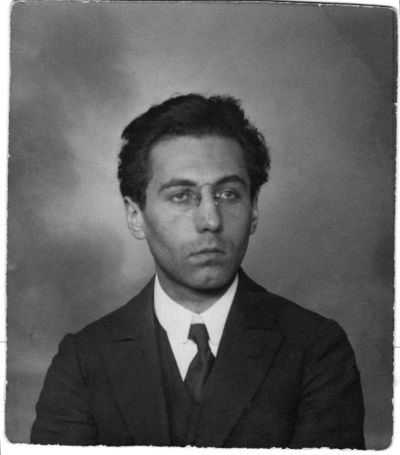
In 1755 Chodowiecki married a woman by the name of Jeanne Barez (1726-1785), who was part of the French colony in Berlin. In 1757 he began experimenting in intaglio printing as can be seen from the fact that his first etching was dated in the same year. Based on one of his earliest intaglios, he probably finished his earliest oil painting in 1758: “A Young Peasant with a Bandaged Face” (National Museum Danzig / Muzeum Narodowe w Gdańsku). In the summer of the same year he began studying drawings of natural anatomy and specialised in red chalk and pencil drawings of women doing domestic work. However, after the birth of his first child in 1761, his interest in this theme began to wane. The Chodowieckis had five children in all, the last of whom was born in 1770: all of them were later artists of one kind or another. In 1764 Daniel was named a member of the Royal Prussian Academy of Arts and Mechanical Sciences in Berlin. After his first creative periods as an etcher between 1758 and 59 and 1763 and 64, he began a continuous period of small format etchings in 1767. The result was more than 2000 works. That said, he earned the necessary livelihood to support his family mainly from cameo portraits and porcelain painting on tins.[5] In 1773 he travelled to Danzig and Silesia. In the same year he met up with two artist friends in Dresden, Anton Graff (1736-1813) and Adrian Zingg (1734-1816). In 1779 the first list of his etchings was published, and in the following year he published his autobiography. After his mother’s death he travelled once more to Danzig in 1780. From 1782 onwards he was committed to reforming the Berlin Academy and he managed to push through these reforms in 1786 as its secretary and one of the six rectors. In 1790 he became a vice- principal, and in 1797 he succeeded Bernhard Rode as the Director of the Academy. Daniel Chodowiecki died in Berlin on 7th February 1801. (Ill. 1)
[1] Daniel Chodowiecki’ letters to the Countess Christiane von Solms-Laubach, edited by Charlotte Steinbrucker, Straßburg 1927, page 180. Already quoted in the book, Chodowiecki. Zwischen Rokoko und Romantik [1916], page 71
[2] For comprehensive deatils on Daniel Chodowiecki ancestors, see Maria Bogucka 1997, pages 33-36
[3] Helmut Börsch-Supan 1998, page 605
[4] Klassik Stiftung Weimar, Kunstsammlungen. Pictured in Elżbieta Budzińska 1986, illustration 1
[5] Martin Klar: Porcelain box by von Daniel Chodowiecki, in: Pantheon. Internationale Jahreszeitschrift für Kunst, München 1931, pages 38-44























































































